

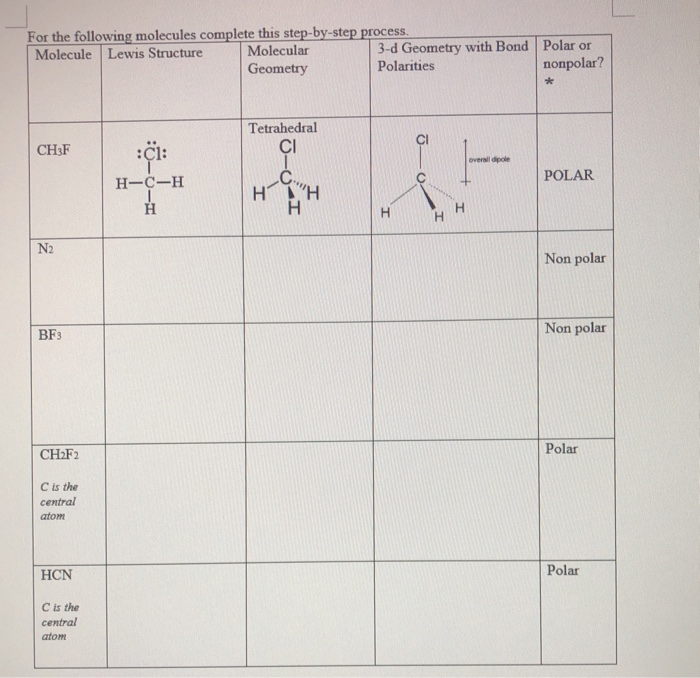
Valance electrons are electrons in the outermost shell that are vital for bonding and forming molecules. These valence electrons either share or are transferred (completely or partially) for bond formation. Only valence shell electrons involve in bond formation. Valence electrons are the total number of electrons present in the atom’s outermost shell. This blog article will help you understand the HCN lewis structure, hybridization, molecular geometry, and molecular orbital diagram.īefore going towards the HCN Lewis structure, let us understand some general terms used in it. It has a linear geometry with a triple bond between carbon (C) and nitrogen (N). The components of this weak acid are carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen. It’s a liquid that has no color, is exceedingly combustible, and is poisonous. The B–B bond length is 1.76 Å.Prussic acid is another name for hydrogen cyanide or HCN. In the tenth B site, B is bonded in a 9-coordinate geometry to six Mg and three B atoms. In the ninth B site, B is bonded in a 9-coordinate geometry to six Mg and three B atoms. In the eighth B site, B is bonded in a 9-coordinate geometry to one Li, five Mg, and three B atoms. There is one shorter (1.76 Å) and one longer (1.77 Å) B–B bond length. In the seventh B site, B is bonded in a 9-coordinate geometry to six Mg and three B atoms. There is one shorter (1.75 Å) and one longer (1.79 Å) B–B bond length. In the sixth B site, B is bonded in a 9-coordinate geometry to one Li, five Mg, and three B atoms.
In the fifth B site, B is bonded in a 9-coordinate geometry to one Li, five Mg, and three B atoms.
In the fourth B site, B is bonded in a 9-coordinate geometry to one Li, five Mg, and three B atoms. In the third B site, B is bonded in a 9-coordinate geometry to one Li, five Mg, and three B atoms. In the second B site, B is bonded in a 9-coordinate geometry to six Mg and three B atoms. In the first B site, B is bonded in a 9-coordinate geometry to one Li, five Mg, and three B atoms. There are a spread of Mg–B bond distances ranging from 2.48–2.52 Å. In the fifth Mg site, Mg is bonded to twelve B atoms to form MgB12 cuboctahedra that share an edgeedge with one LiB12 cuboctahedra, edges with eleven MgB12 cuboctahedra, a faceface with one LiB12 cuboctahedra, and faces with seven MgB12 cuboctahedra. There are a spread of Mg–B bond distances ranging from 2.47–2.51 Å. In the fourth Mg site, Mg is bonded to twelve B atoms to form MgB12 cuboctahedra that share an edgeedge with one LiB12 cuboctahedra, edges with eleven MgB12 cuboctahedra, a faceface with one LiB12 cuboctahedra, and faces with seven MgB12 cuboctahedra. There are a spread of Mg–B bond distances ranging from 2.48–2.51 Å. In the third Mg site, Mg is bonded to twelve B atoms to form MgB12 cuboctahedra that share an edgeedge with one LiB12 cuboctahedra, edges with eleven MgB12 cuboctahedra, a faceface with one LiB12 cuboctahedra, and faces with seven MgB12 cuboctahedra. There are a spread of Mg–B bond distances ranging from 2.49–2.51 Å. In the second Mg site, Mg is bonded to twelve B atoms to form MgB12 cuboctahedra that share edges with three equivalent LiB12 cuboctahedra, edges with nine MgB12 cuboctahedra, and faces with eight MgB12 cuboctahedra. There are a spread of more » Mg–B bond distances ranging from 2.48–2.50 Å. In the first Mg site, Mg is bonded to twelve B atoms to form MgB12 cuboctahedra that share edges with twelve MgB12 cuboctahedra, faces with two equivalent LiB12 cuboctahedra, and faces with six MgB12 cuboctahedra. There are a spread of Li–B bond distances ranging from 2.48–2.50 Å. Li is bonded to twelve B atoms to form LiB12 cuboctahedra that share edges with twelve MgB12 cuboctahedra and faces with eight MgB12 cuboctahedra. LiMg9B20 is hexagonal omega structure-derived structured and crystallizes in the triclinic P-1 space group.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
